Everything you don’t know about ectopic pregnancy!

The most dangerous type of pregnancy among women is ectopic pregnancy. It occurs when an embryo (fertilized egg) develops in the wrong place outside the uterus, such as in the fallopian tube or attached to the ovary, an ectopic pregnancy always ends in miscarriage. Without treatment, it can lead to heavy bleeding and even death for the woman.
If you have symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy, such as vaginal bleeding or pelvic pain, contact your doctor right away. Of course, there is no reason to worry because today, with the advancement of medical science, many women who have experienced an ectopic pregnancy can have a healthy pregnancy afterward.
Related posts: Iodine consumption during pregnancy
Familiarity with an early natural pregnancy.
Normally, an egg is released from the ovary into the fallopian tube. This process is called ovulation and usually occurs once a month, around the middle of your period. Sperm can also live in the fallopian tubes for up to five days after intercourse.
A sperm can then combine with an egg (fertilization) and create an embryo. The tiny embryo is pulled along a fallopian tube towards the uterus by tiny hairs (cilia). It usually attaches to the lining of the uterus and develops into a baby.
If you have experienced such an incident, it is best to go to a gynecologist as soon as possible or start your treatment process as soon as possible through an online consultation with a gynecologist.
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
Ectopic means “out of place”. Ectopic pregnancy is when the fetus grows in an inappropriate place outside the uterus.
As mentioned, an embryo is a fertilized egg that is created by combining an egg and a sperm. When the egg is fertilized, it usually travels down the fallopian tube and attaches itself to the uterine lining. The fallopian tubes are the tubes between the ovaries (where the eggs are stored) and the uterus.
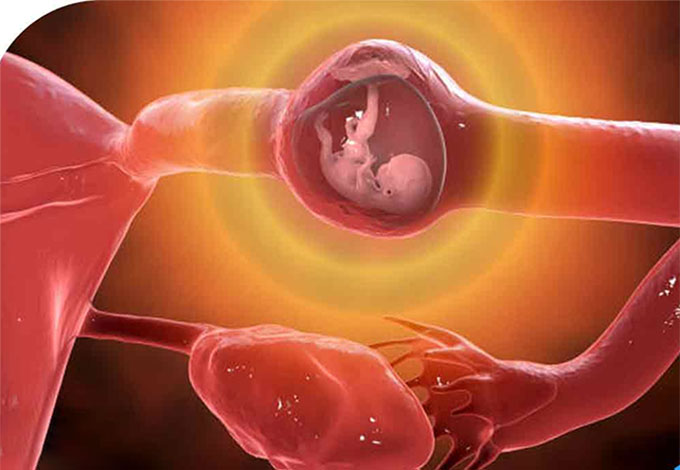
In most ectopic pregnancies, the fertilized egg attaches itself to the fallopian tube before reaching the uterus. In fewer cases, it attaches to the ovary, cervix, or abdomen. The cervix is located above the vagina.
These areas don’t have enough space or adequate tissue for the baby to grow. Without treatment, an ectopic pregnancy can cause heavy bleeding or rupture of the junction, and in some cases, it can also lead to severe bleeding and even death of the pregnant woman. This unpleasant event always ends in the loss of the fetus.
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
First of all, it is better to know that if you have a combination of the following symptoms and think you may be pregnant, even if you have not had a positive pregnancy test, contact your gynecologist as soon as possible.
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy usually appear between the fourth and twelfth week of pregnancy.
-
vaginal bleeding
Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy is slightly different from your period. It often starts and stops and can be watery and dark brown in color. Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy can be common and not necessarily a sign of a serious problem, but you should always see a doctor if you have any.
-
Feel pain
You may have stomach pain, usually on one side. It can develop suddenly or gradually and can be persistent or come and go.
-
Shoulder tip pain
Shoulder tip pain is an unusual pain that is felt where the shoulder ends and the arm begins. If you have experience, you should see a doctor right away.
We don’t fully understand why this pain occurs. It is believed to be associated with the leakage of fluid or blood into the pelvis or lower abdomen, which occurs in an ectopic pregnancy.
There are nerves in this area that connect to your shoulder. Stimulation of these nerves can cause pain in the tip of the shoulder.
-
Discomfort when going to the toilet
You may feel pain when you vomit or have a bowel movement. You may also have diarrhea or constipation. Some changes in the normal pattern of the bladder and bowels are normal during pregnancy. These symptoms can be caused by urinary tract infections and stomach problems. But it’s still a good idea to seek medical advice.
The cause of ectopic pregnancy
Usually, an ectopic pregnancy occurs because the fertilized egg cannot move quickly through the fallopian tube. Infection or inflammation in the tube can cause partial or complete blockage. This is usually caused by pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
Another common cause of tubal blockage is endometriosis. This is when cells from the lining of the uterus grow outside the uterus. The cells can grow inside the fallopian tube and cause a blockage. Scar tissue from previous abdominal surgery or fallopian tube surgery can also block the tube.
Risk factors for ectopic pregnancy
Here are 10 possible risk factors for an ectopic pregnancy.
- Age: An ectopic pregnancy can occur in any woman of any age who is ovulating and sexually active with her male partner. The highest probability of ectopic pregnancy occurs in women aged 35-44 years.
- History: The biggest risk factor for ectopic pregnancy is a previous history of ectopic pregnancy.
- Abnormalities of the fallopian tubes: Any disturbance in the normal structure of the fallopian tubes can be a risk factor for tubal pregnancy or ectopic pregnancy elsewhere.
- Previous gynecological operations: Previous fallopian tube surgery, such as tubal sterilization or reconstructive procedures, can lead to scarring and disruption of normal tubal anatomy, increasing the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Infections: Infection in the pelvis (pelvic inflammatory disease) is another risk factor for ectopic pregnancy. Pelvic infections are usually caused by sexually transmitted organisms such as chlamydia or the bacteria that cause gonorrhea. However, non-sexual bacteria can also cause pelvic infections and increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy. This infection causes an ectopic pregnancy by damaging or blocking the fallopian tubes. Normally, the inner lining of the fallopian tubes is lined with tiny hair-like protrusions called cilia. These cilia are important for the fluid transfer of the egg from the ovary through the fallopian tube to the uterus. If these cilia are damaged by the infection, egg transport is stopped. A fertilized egg can in the fallopian tube without reaching the uterus, resulting ectopic pregnancy. In the same way, the scar caused by infection and partial blockage of the fallopian tubes can also prevent the egg from reaching the uterus.
- Multiple sexual partners: Since having multiple sexual partners increases the risk of pelvic infection in women, multiple sexual partners are also associated with an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Obstetrics and Gynecology conditions: such as pelvic infections, conditions such as endometriosis, fibroids, or pelvic scar tissue (pelvic adhesions), can narrow the fallopian tubes and interfere with egg transport, increasing the chance of an ectopic pregnancy.
- IUD use: About half of the pregnancies in women who use intrauterine devices (IUDs) are ectopic. However, the total number of women who get pregnant using an IUD is very small. Therefore, the total number of IUD-related ectopic pregnancies is very low.
- Smoking: Smoking around the time of conception is also associated with an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy. This means that the risk depends on each woman’s habits and increases with the number of cigarettes consumed.
- Sterility: A history of infertility for two years or more is also associated with an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Other causes: Infections, birth defects, or tumors of the fallopian tubes can increase a woman’s risk of having an ectopic pregnancy.
Possible complications of ectopic pregnancy
The pregnancy often goes away after a few days. About half of ectopic pregnancies probably end this way. You may have no symptoms and may never know you are pregnant. Sometimes there is mild pain and vaginal bleeding similar to a miscarriage. If this happens, you don’t need to do anything else.
A pregnancy can grow in the narrow fallopian tube for some time. This can stretch the tube and cause symptoms. This is when an ectopic pregnancy is usually diagnosed. The narrow fallopian tube can only stretch a little. If the pregnancy continues to grow, the fallopian tube usually splits (ruptures). This can cause internal bleeding and severe pain. This is a medical emergency.
Treatment strategies for ectopic pregnancy
Treatment options for ectopic pregnancy include observation, laparoscopy, laparotomy, and medications. The choice of these options by the attending physician is different for each person, depending on various factors.
Some ectopic pregnancies resolve on their own without requiring any intervention, while others require immediate surgery due to life-threatening bleeding. However, due to the risk of rupture and potentially serious consequences, most women diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy are treated with medication or surgery.
pharmacological therapy
For ectopic pregnancy, it involves using a cancer drug called methotrexate (Rumatex, Trexal).
Medical treatment for ectopic pregnancy includes the use of an anticancer drug called methotrexate (Rumatex, Trexal). Medical treatment may also be successful in treating a certain group of women who have an ectopic pregnancy. Medical treatment involves the use of an anticancer drug called methotrexate (Rheumatrex, Trexal). This drug works by destroying the growing cells of the placenta, thus causing the miscarriage of an ectopic pregnancy.
Some patients may not respond to methotrexate and require surgical treatment. Methotrexate is gaining popularity due to its high success rate and low side effects.
There are a few factors, including the size of the mass associated with an ectopic pregnancy and the concentration of beta-HCG in the blood, that help doctors decide which women are candidates for medical treatment rather than surgery. Optimal candidates for methotrexate treatment are women with a beta subunit (HCG) concentration of less than or equal to 5000 mIU/mL.
In a properly selected patient population, methotrexate therapy is approximately 90% effective in the treatment of ectopic pregnancy. There is no evidence that the use of this medicine has any side effects in subsequent pregnancies. Additional tests (HCG) are usually requested to confirm that methotrexate treatment is working.
surgery
If an ectopic pregnancy has ruptured a tube, emergency surgery is required. Sometimes surgery is needed even if the fallopian tube is not ruptured. In these cases, the ectopic tubal pregnancy may be removed or the entire tube with the pregnancy may be removed. Surgery is usually performed laparoscopically.
In this method, a narrow, lighted camera is used, which is inserted through small incisions in the abdomen. It is performed in the hospital under general anesthesia. Your gynecologist will talk to you about the possible side effects and risks of surgery for an ectopic pregnancy. These can include pain, fatigue, bleeding, and infection.
For those who need surgery, the most common treatment is surgery. Two surgical options are available.
- laparotomy
- Laparoscopy
Prevention is better than cure
First of all, it’s best to know that you cannot prevent an ectopic pregnancy, but you can try to control your risk factors. Don’t smoke, if you smoke, plan to quit before you get pregnant. Use condoms during sexual intercourse before pregnancy.
This can help prevent sexually transmitted infections, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, which can cause PID. If you are at risk for an ectopic pregnancy, talk to your doctor. You can take additional steps to detect an ectopic pregnancy early.
This could include having your hormone levels checked or scheduling an ultrasound ahead of time.
Frequent questions
How common is an ectopic pregnancy?
About 1 to 2 percent of all pregnancies in the general population are ectopic, but the rate is highest among those receiving assisted reproductive technology (ART), at 2 to 5 percent. Most ectopic pregnancies (90%) occur in the fallopian tubes, but 10% occur in the ovary, the outer lining of the uterus, the spaces between the fallopian tubes, the abdominal cavity, or inside a cesarean section scar.
Can an ectopic pregnancy be completed?
Although there have been a few reported cases of cesarean delivery by women with live ectopic babies, this is extremely rare. The possibility of ectopic pregnancy until the end of the term is so remote and the risk to the woman is so great that it can never be recommended.
It would be ideal if an ectopic pregnancy in the fallopian tube could be surgically rescued to be transferred to the uterus. This concept has not yet been accepted as a successful method.
Overall, great progress has been made in the early diagnosis and treatment of ectopic pregnancy, and the mortality rate from this condition has decreased dramatically.
What drug is used to treat ectopic pregnancy?
The most common drug used to treat ectopic pregnancy is methotrexate. This medicine stops the growth of cells, which ends the pregnancy. The pregnancy is then absorbed by the body within 4 to 6 weeks. This does not require the removal of the fallopian tubes.
When is a drug used to treat ectopic pregnancy?
If the pregnancy has not ruptured the fallopian tube, methotrexate may be used. Several factors play a role in the decision to use methotrexate. One of the most important factors is your ability to follow blood tests that check blood levels of HCG. You cannot use methotrexate if you are breastfeeding or have certain health problems.
How can I get emotional support after an ectopic pregnancy?
For some women, an ectopic pregnancy can be traumatic. You may struggle with many emotions after an ectopic pregnancy, even if you did not intend to get pregnant. Take some time to sort out your feelings. Counseling can be helpful.
Ask your gynecologist or other specialists in this field for a referral to a consultant. Online counseling can also be a place to get support from other women who have had an ectopic pregnancy.
Can an ectopic pregnancy affect future pregnancies?
Once you have had an ectopic pregnancy, you are at an increased risk of having another pregnancy. During future pregnancies, pay attention to the signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy until your ob-gyn confirms that your next pregnancy is developing in the right place.
How is life with an ectopic pregnancy?
Whether treated with medication or surgery, recovery can take several weeks. You may feel tired and have pain or discomfort in your abdomen. You may feel pregnant for a while longer. It takes some time for the levels of HCG in your body to decrease. It will probably take a few cycles for your periods to return to normal.
If you have had an ectopic pregnancy, there is a possibility of another pregnancy. You may even have trouble getting pregnant again. Before trying to get pregnant after an ectopic pregnancy, you need to give yourself time to heal.
Having an ectopic pregnancy can be emotionally difficult. You may feel sad, angry, and confused. Talk about your feelings with your partner, trusted family member, or friend. Take the time to find a family member or friend to talk to about your feelings. Allow yourself to grieve the loss of your pregnancy.
What happens if you don't know you have an ectopic pregnancy?
How long can you have an ectopic pregnancy without knowing?
What are the 3 causes of an ectopic pregnancy?
Can an ectopic pregnancy remove itself?
Summary
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the embryo implants itself in tissue outside the uterus, often in the fallopian tubes. Without prompt treatment, this can lead to life-threatening complications for the pregnant woman.
However, treatment cannot save the pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancy symptoms can start as early as week 4 and as late as week 12.
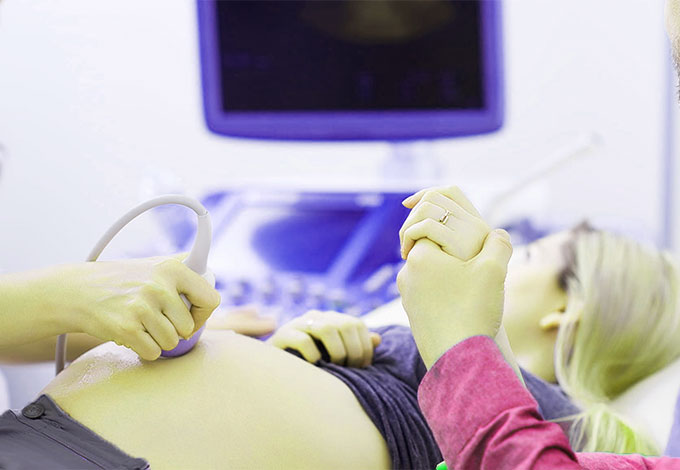
Diagnosing this problem may involve a combination of pregnancy testing, symptom assessment, and ultrasound. Early diagnosis can reduce the risk of complications, including fallopian tube damage and internal bleeding. Treatment may include surgery, but when an ectopic pregnancy is detected early by a doctor, drug treatment may be an option.
