Dilation and curettage
Curettage is a medical procedure used to remove tissue or growths from inside the uterus, usually during a miscarriage or abortion.
The procedure involves using a curette, a small, spoon-shaped instrument, to scrape the lining of the uterus and remove any remaining tissue. Curettage may also be used to diagnose and treat certain conditions such as abnormal uterine bleeding or the removal of polyps.
While it is a relatively safe and effective procedure, there are potential risks such as infection, bleeding, and perforation of the uterus. Therefore, it is important for patients to carefully consider the benefits and risks before undergoing curettage.
Related posts: 5 ways to determine the best time to get pregnant
What is curettage?
Dilation and Curettage or D&C is a minor surgical procedure in which the cervix is slightly opened and a series of special tools are used to scrape the lining of the uterus. In this article, we have mentioned everything you need to know about this process.
Reasons and types of curettage
Dilation and curettage are used to diagnose or treat some uterine diseases. In this section, we have discussed the types of curettage and the reason for performing each type of curettage.
Diagnostic curettage
Diagnostic dilation and curettage is a procedure during which the cervix is opened so that the doctor can take samples from the uterus. Your doctor may recommend a procedure called endometrial biopsy or endometrial sampling to diagnose the disease. The endometrial sampling process is usually performed in the following cases. If:
- You have abnormal uterine bleeding.
- You have postmenopausal bleeding.
- You have abnormal endometrial cells that are seen during routine screening for cervical cancer.
To perform this test, the doctor collects a tissue sample from the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium). Then he sends this sample to the laboratory for further examination. This test can detect the following disorders:
Endometrial hyperplasia (endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia) is a precancerous condition in which the lining of the uterus becomes too thick.
Related posts: Eczema around the mouth in pregnancy
Therapeutic curettage
When a curettage procedure is performed to treat a condition, the doctor removes the contents of the uterus instead of a small biopsy. This process may be done for the following purposes:
- left in the uterus after an abortion may cause infection or severe bleeding. To prevent these symptoms, curettage is used to clear these tissues.
- Removal of a tumor that developed in a molar pregnancy.
- Removal of cervical or uterine polyps, which are usually non-cancerous (benign).
- A curettage procedure treats excessive bleeding after delivery by removing the placenta that remains in the uterus.
- To remove the intrauterine device (IUD), which is a contraceptive method.
This process is performed by a doctor specializing in obstetrics and gynecology or a doctor specializing in obstetrics.
Measures before the curettage process
You can perform the curettage procedure in a doctor’s office, clinic, or hospital on an outpatient basis. This process usually only takes 10 to 15 minutes, but you may need to stay under observation for up to five hours.
Before the curettage, the doctor will perform an examination and ask about your medical history. It will also ask you to sign a consent form. Before the procedure, ask your doctor any questions you have about curettage.

Be sure to inform your doctor if you have any of the following. If:
- It is possible that you are pregnant.
- You are allergic to iodine, latex, and any medicine.
- Do you have a history of bleeding disorders or are you taking blood thinners
After these steps, you will receive an anesthetic and your doctor will discuss the type of anesthesia with you. The type of anesthesia depends on the treatment procedure you need.
- If you receive general anesthesia, you will not be awake during the procedure.
- If you receive spinal or epidural (regional) anesthesia, you will be numb from the waist down.
- If you receive local anesthesia, you will be awake during the procedure while the area around your cervix is numbed.
- Before the curettage, you may need to undress, put on a gown, and empty your bladder.
Important points before the curettage process
Depending on the type of anesthesia used, the doctor will give you instructions before the curettage, some of which include the following:
Not taking unnecessary drugs
You should stop taking medications such as aspirin (which can increase the risk of bleeding) and any over-the-counter medications (such as cold medicines and laxatives) a few days before the curettage. Avoid alcohol and tobacco. Many surgeons advise patients to stop taking herbal supplements at least two weeks before surgery. Tell your doctor about all the medications you are taking.
Chronic Diseases
Your doctor will ask you to tell him about any chronic diseases you have before this procedure. For example, if you have uncontrolled high blood pressure, your doctor may prescribe a detailed treatment plan for you in and out of the hospital to improve your blood pressure. This is important to avoid any side effects during the curettage process.
Eating and drinking restrictions
If you are going to undergo general anesthesia, your doctor will ask you not to eat or drink anything for 12 hours before the procedure. For local or regional anesthesia, you should not eat or drink anything for 8 hours before.
Preliminary tests
On the day before the operation or on the day of the operation, the doctor may ask you to do routine tests such as blood, urine, and other tests to make sure that there is no disease and the curettage can be done without worry.
Curettage procedure
The curettage process usually includes the following steps:
First, you should lie on your back on the examination bed while your feet are placed on the stirrups of the bed. These stirrups keep the legs open in a suitable position so that the doctor can have easier access to the treated area (the position of the legs should be the same as when the doctor performs a pelvic examination).
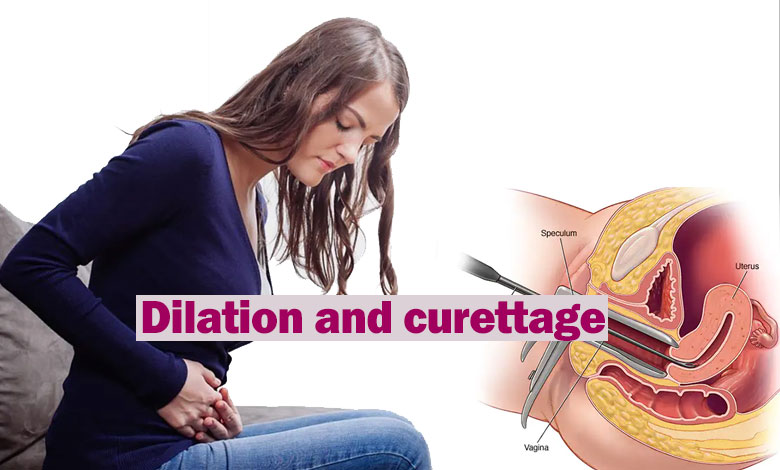
In the next step, a tool called a speculum is inserted into the vagina to separate the walls of the vagina and reveal the cervix.
The doctor then cleans the cervix with an antiseptic solution.
For local anesthesia, the doctor injects medicine using a small needle to numb the area.
For general or regional anesthesia, the anesthesiologist continuously monitors the person’s heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, and blood oxygen levels during surgery.
A type of surgical forceps called a Tenaculum may be used to hold the cervix steady during this procedure.
If the cervical tissue needs further investigation, the inside of the cervical canal may be scraped with a small surgical curette.
A thin rod-like instrument called a uterine catheter is inserted through the cervix to determine the length of the uterus. If you are under local anesthesia, the placement of this tool may cause muscle cramps in the uterine area. Then the doctor removes this tube.
The cervix is opened and widened (dilated) by inserting a series of thin rods. The diameter of each bar will be larger than the previous bar. This procedure gradually enlarges the cervix until a curette (spoon-shaped instrument) can be inserted into the cervix.
Then the curette enters the uterus through the cervix and the sharp spoon-shaped edges of the curl pass through the lining of the uterus to scrape the tissues. In some cases, suction may be used to remove tissue. If you are under local anesthesia, this step may also lead to muscle cramps.
In some cases, the doctor may dilate and open the cervix a few hours or even a day before the curettage. This helps to gradually open the cervix and is usually done when the cervix needs to open more than standard (such as for abortion or certain types of hysteroscopy).
To improve dilatation, sometimes the doctor uses a drug called misoprostol (Cytotec), which is given orally or vaginally. This medicine helps to soften the cervix. Another method of dilation is to insert a thin rod made of laminaria into the cervix. By absorbing the liquid in the cervix, laminaria gradually expands and causes the cervix to open.
Complications of curettage
Although rarely, the curettage process is associated with the possibility of some side effects, including:
Infection
There is always a chance of infection when an instrument is inserted into the uterus. Most infections can be easily treated with antibiotics. This infection may be caused by bacteria that are transferred from the vagina to the uterus during or after this procedure.
Symptoms of infection often include vaginal discharge, cramping and pain in the uterus, and fever. If treated immediately, the infection does not cause long-term complications. However, sometimes the infection can cause scarring in the uterus, fallopian tubes, or ovaries, which can make it difficult to get pregnant in the future.
Perforation of the uterus
Although this complication is rare, it is common in women who have the following conditions at the time of this procedure:
- Women who have a uterine infection
- Elderly women who are postmenopausal.
- If this procedure is done for abortion
If the doctor suspects the existence of this complication, he asks the patient to stay in the hospital for observation or surgery.
Asherman syndrome
This is a rare complication that involves the formation of scar tissue in the uterus. Sharman’s syndrome is caused by aggressive scratching or the body’s abnormal reaction to scratching. In this condition, thick wounds are created that can completely fill the uterus. This situation may cause infertility and interruption of menstrual periods.
Undiagnosed disease
Since the curettage process cannot completely remove the endometrium (the lining of the uterus), there is a possibility that a person’s disease may go undiagnosed. This is why this procedure is often performed along with hysteroscopy (examination of the lining of the uterus with the help of an instrument that allows imaging).
Damage to the cervix
If the cervix tears during the curettage process, the doctor may recommend applying pressure or medication to stop the bleeding. Sometimes he closes the wound with stitches. If the cervix is softened using medicine before the curettage process, this complication may be prevented.
Recovery after curettage
Usually, all women who undergo a curettage can return to their normal daily activities after two days
The recovery process after curettage is usually short. Recovery time will vary depending on the type of operation performed and the type of anesthesia used.
If you are under regional or general anesthesia, you will be taken to the recovery room for observation. When your blood pressure, pulse, and breathing are stable and you are conscious, you will be transferred to the inpatient ward or you will be discharged.
After the curettage is performed using local anesthesia, you may need to rest and be monitored for about two hours before going home.
Care after fetal curettage
Some of the care points that the doctor recommends after the curettage include the following:
- It is usually recommended to avoid vaginal douching for two to three days after the curettage or for the period recommended by the doctor.
- You may also need to observe some restrictions regarding your physical activity (including no vigorous activity or heavy lifting).
- After the curettage, you can resume your normal diet unless the doctor recommends otherwise.
- Pain and muscle cramps (similar to menstrual cramps) will probably be the strongest feeling of the patient immediately after the curettage process. Although most women only experience pain and cramping for an hour, some women may have it for a day or more.
- It is recommended that the patient does not drive for at least 24 hours after anesthesia. It is best to follow this advice after local anesthesia as well because the side effects of anesthetic drugs can temporarily disrupt the body’s coordination and response time. In this situation, it is better to ask a friend or family member to take you home.
- Naproxen or ibuprofen is usually prescribed to relieve pain and muscle cramps after curettage. Narcotics are rarely needed for pain after curettage. Aspirin and some types of pain relievers increase the risk of bleeding, so make sure you only take the prescribed medication.
- Even if you feel pain and discomfort, it is better to get up and move as soon as possible. This keeps the muscles strong and helps prevent blood clots from forming in the legs.
It is recommended not to go to work or university for at least two days after the curettage and rest at home to recover faster.
Bleeding after curettage
Slight vaginal spotting or bleeding is normal for a few days after the curettage. Rarely does a person experience severe bleeding that requires a blood transfusion. But if the tools used during the dilation and curettage process damage the walls of the uterus, bleeding may occur. Bleeding may also occur if an undetected fibroid is cut during the procedure.
If two or more sanitary napkins or tampons become completely soaked with blood within two hours and the bleeding continues, call your doctor or go to the emergency room.
Risks of curettage
The doctor does not perform curettage in the following situations, except in emergency cases:
Pelvic infection:
If you have a genital infection, it is possible that surgical instruments inserted into the vagina and cervix may transfer bacteria from the vagina or cervix into the uterus. There is also the possibility of damaging the infected tissue. For this reason, your doctor may recommend that you wait until the infection is completely gone with antibiotics before performing a curettage.
Blood clotting disorders:
Stopping bleeding after curettage depends largely on the body’s natural ability to clot blood; Therefore, women who have some specific disorders related to the blood usually should not do this procedure.
Serious diseases:
For example, heart and lung diseases can make general anesthesia and sometimes local anesthesia dangerous.
Call your doctor if you experience the following symptoms after the curettage procedure:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness that continues and worsens.
- Fever
- Muscle pain and cramps that last more than 48 hours.
- Pain that gets worse instead of getting better.
- Foul-smelling discharge from the vagina
Pregnancy after curettage
Many women are worried about the damage to the uterus after the curettage process. But can performing a curettage really have a negative effect on future fertility? According to the doctors, if the curettage process is done correctly, it will not have any negative effect on future fertility.
In general, there are two very rare events associated with curettage that can reduce the chance of pregnancy. First, if a person suffers from infections related to this process while performing the curettage, he may suffer from adhesions of the uterus.
Uterine adhesions can significantly reduce the chance of getting pregnant in the future. Uterine adhesions (also known as Asherman’s syndrome) occur when scar tissue builds up between the inner walls of the uterus, causing the walls to stick together.

Also, if the person has had several miscarriages in the past, this situation makes them more prone to not getting pregnant. Although some patients with recurrent miscarriages think that the curettage procedure causes fertility problems, it is actually multiple and recurrent miscarriages that are associated with future miscarriages.
According to doctors, if a person has had a miscarriage, it is better to perform the curettage process than to allow the uterus to clean itself.
One study found that nearly 90 percent of women who underwent a curettage were able to conceive within a year of trying to conceive again.
If I had a miscarriage, do I need dilation and curettage?
About half of the women who experience miscarriage do not need a dilation or curettage. An abortion that occurred before the 10th week of pregnancy is likely to be a spontaneous abortion and will not cause any problems. After the 10th week of pregnancy, the possibility of incomplete abortion is higher. In this case, you need a curettage procedure to ensure that the uterus is cleared.
You can decide whether you want to have a natural abortion or a curettage. In this situation, it is better to consult your doctor. Your doctor will help you decide which method is best for you.
Do dilation and curettage affect the menstrual cycle?
Since the curettage removes the lining of the uterus, the lining must be regenerated. Therefore, after the curettage, your next period may be earlier or later than usual. In this situation, you should avoid using tampons or having sex for some time after the curettage.
Until the cervix returns to its normal, closed state, you are more at risk of bacteria entering the vagina and getting an infection. Your doctor will tell you when you can resume having sex and using tampons.
Is it necessary to visit the doctor again after the curettage process?
If the doctor has removed tumors or cancerous material using curettage, you will receive your test results sometime later. If the results are benign (non-cancerous), there is usually no need to return. But if the results show cancerous or precancerous cells, your doctor will likely refer you to a specialist to guide you on the next steps in your treatment.
What should I do after the curettage?
To weeks after your procedure, or a few days after bleeding has stopped :
- Shower instead of taking a bath
- Avoid sexual intercourse
- Use sanitary pads instead of tampons
- Avoid going swimming
- If you experience any signs of infection, see your doctor immediately.
How long does it take for curettage to heal?
How long does it take for the uterus to heal after D&C?
Can I take a bath after the curettage?
Conclusion
In conclusion, curettage is a common medical procedure used to remove abnormal tissue from the uterine lining, such as in cases of abnormal bleeding or during a miscarriage.
It is generally a safe and effective procedure, although there are risks associated with any medical procedure. Proper aftercare following a curettage procedure is crucial to reduce the risk of complications and ensure a successful recovery.
Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions closely, which may include taking pain medication, avoiding sexual intercourse for a certain period of time, and monitoring for any signs of infection or other complications. With proper care, most patients can expect to recover fully from a curettage procedure within a few weeks.
